“The subjective result of bouncing sound off the screen is a very profound distortion. The sound isn’t crisp and tight and clear. It’s smeared in time.”
Video walls have become a big status thing—and an even bigger investment—but getting them to sound good isn’t as easy as you might think
by Steve Haas
June 24, 2022
While most companies don’t yet heavily promote that they sell their video walls for residential use, you’d be hardpressed to find a luxury integrator who isn’t installing them in high-end homes. But they present an interesting challenge. They can often take up an entire wall, but you don’t have the option of putting speakers behind them like you do with a projection screen. Acoustician Steve Haas of SH Acoustics has checked out many of the existing audio solutions for LED walls and found them all wanting. But realizing that video walls are quickly becoming the likely future of viewing in premium home entertainment spaces, he’s been more than motivated to try to determine who has the best approach and how it can be optimized.
—ed.
The question of how to achieve good sound with a video wall isn’t a new one but the latest version of the problem of what to do with sound when you’re dealing with any kind of solid screen. While many projection screens are created with holes that allow the sound to come through when speakers are placed behind them, many are not, in order to maximize light gain and other aspects of video reproduction.
LED and Micro-Tile video walls have existed in commercial spaces like museums for quite some time. Between our work with those and with multimedia theaters with solid screens, we’ve had to design plenty of workarounds to match the quality of the ideal “speaker behind acoustically transparent screen” approach. When the video contains dialogue with talking heads, we’ve achieved decent success by placing the speakers above and below and then using vertical panning techniques for the audio. If there’s no dialogue, we have a lot more liberty to simply deliver sound from above or below, or even reflect it off the screen. But these approaches definitely result in some degree of compromise. So when a leading speaker manufacturer developed a system for reflecting the sound from speakers mounted to the ceiling off the LED wall, we had a good understanding of the challenges involved in making that work efficiently.
We have several issues with this approach that stem from the fact that speakers radiate sound off the sides and rear of their cabinets differently at different frequencies. Higher frequencies will be directed right at the LED wall, but lower frequencies will reflect from most speakers boxes and combine with the same frequencies that are also projecting from the front of the speaker. In museum installations, we often have the room to put big barrier clouds below the speakers so the sound coming off their cabinets isn’t audible over the sound of what’s being reflected.

Having a solid screen in this exhibition area at the Kennedy Space Center Exploration Space gallery meant speakers couldn’t be placed behind the screen but had to be positioned above and below it instead.
photo | BRC Imagination Arts
Even if you can ignore having three large speakers hanging from the ceiling shrouded in multiple layers of plywood sandwiched with other damping materials, the listener can still hear those lower frequencies coming from the backs of the speakers before they bounce off the screen along with the upper midrange and treble. The subjective result is a very profound distortion of the sound. It’s not crisp and tight and clear. It’s smeared in time.
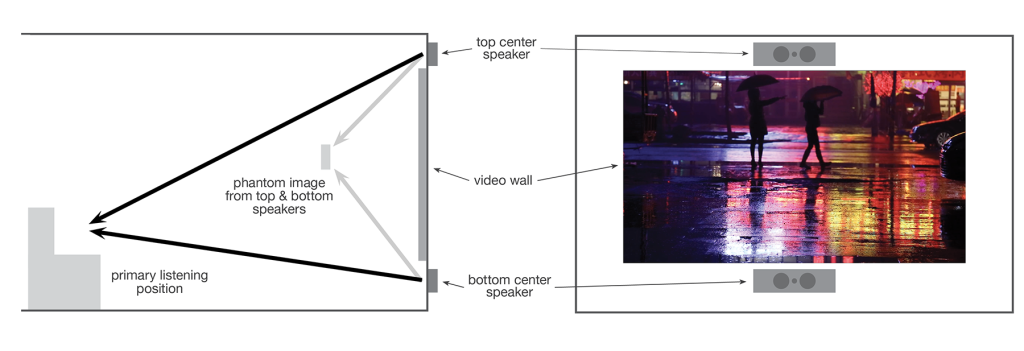
A number of speaker manufacturers are developing reformatted speakers that fit into a tight space below or above a video wall, and Wisdom Audio, Ascendo, and others have come out with completely new products that are meant to address the LED wall market. The issue is: Do you place those speakers above the screen, below the screen—or both?
There are times when a bottom placement would work, mainly in a media room with a couch and no second row. Then there are times when top placement could work by itself, if the speakers aren’t jammed up against a hard ceiling and creating strange reflections that cause comb filtering and other distortion if not properly treated. In either case, it’s difficult with only one set of speakers to optimally localize the sound at the proper image height without employing processing techniques developed by the manufacturers. We’re still evaluating the effectiveness of those techniques.
CLICK ON THE IMAGE TO ENLARGE
Sign up for our monthly newsletter
to stay up to date on Cineluxe
The UK-based company TPI offers a variation of the above systems, called the Movement system, which uses speakers designed to fit within very tight boundaries below and above the video wall—something like 8 inches of height for each of them in their smallest configuration. That approach is similar to what other companies are doing, but TPI has also developed a black box that allows you to sit in the primary listening position and change the combination of level and time delay between each pair of top and bottom speakers so you can adjust the height of the sonic image.
This approach—which is much easier than doing the hard calculations of time delay and relative levels between top and bottom speakers—is appealing even to us at SHA, who specialize in that sort of thing. It just takes away one task in an already complicated calibration, and there aren’t too many variables you can mess up.
Our role is to minimize the compromises, and that’s true whether you’re using a projector and screen or an LED wall. It’s really a matter of everybody involved—the display manufacturers, the speaker manufacturers, the dealers, the installers, the calibrators—working together to find an optimal solution. You can’t have a movie without picture and sound, and the picture and sound need to work together. So we have to make them work together and not have either element be an afterthought.
No matter which approach one entertains for delivering audio with a direct-view wall, the experience at all seats in a theater or media room won’t be the same without being able to locate the sound sources directly in line with the image. Fortunately, some variation of sound/image localization can be accepted if all other aspects of the room and system are designed effectively. Advanced calibration of each of the audio system types mentioned above can at least ensure that the row with the primary listening seat(s) will be optimized with the exact sonic image height, while the other rows in front and behind will have as little deviation as possible.
We look forward to continuing this exploration and seeing the variety of manufacturers work to perfect their offerings.
Steve Haas is the Principal Consultant of SH Acoustics, with offices in the NYC & LA areas. Steve has been a leading acoustic and audio design & calibration expert for over 25 years in high-end spaces ranging from home theaters, studios, and live music rooms to major museums and performance venues.

a rendering of the Movement L center speaker, part of the TPI Movement system designed specfically for video wall installations
© 2023 Cineluxe LLC